The CloudStack Kubernetes Provider¶
Introduction¶
The CloudStack Kubernetes Provider facilitates Kubernetes deployments on Cloudstack. It allows Kubernetes to dynamically allocate IP addresses and the respective networking rules on CloudStack to ensure seamless TCP, UDP and TCP-Proxy LoadBalancer deployments on Kubernetes.
It also automatically manages these rules modifying them based on the deployment as well as the size of the cluster.
It was initially the Cloudstack provider in Kubernetes which was later extracted to allow for pluggable providers.
The Prebuilt containers are available on Docker Hub.
Deployment¶
The CloudStack Kubernetes Provider is automatically deployed when a Kuberentes Cluster is created on CloudStack 4.16+
In order to communicate with CloudStack, a separate service user kubeadmin is created in the same account as the cluster owner. The provider uses this user’s API keys to get the details of the cluster as well as update the networking rules. It is imperative that this user is not altered or have its keys regenerated.
The provider can also be manually deployed with instructions here
Further details as well as instructions on how to build and contribute to the project can be found here
Usage¶
In the following example, a LoadBalancer Service is created to balance traffic between the nodes in a cluster. The DaemonSet creates pods and maps the ports on the pods to the same ports on the host. The LoadBalancer creates an externally-accessible IP address that sends traffic to the correct port on the cluster nodes.
The following yaml creates a DaemonSet which brings up a pod on every node and maps port 80 and 443 from the pod to the node. The LoadBalancer Service then creates a public IP to balance traffic on port 80 and 443 between the nodes.
--- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: traefik annotations: service.beta.kubernetes.io/cloudstack-load-balancer-proxy-protocol: enabled spec: type: LoadBalancer ports: - name: http port: 80 targetPort: http - name: https port: 443 targetPort: https --- apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: traefik-conf data: traefik.toml: | defaultEntryPoints = ["http"] [entryPoints] [entryPoints.http] address = ":80" [entryPoints.http.proxyProtocol] trustedIPs = ["127.0.0.1/32", "10.0.0.1/32"] [entryPoints.https] address = ":443" [entryPoints.https.proxyProtocol] trustedIPs = ["127.0.0.1/32", "10.0.0.1/32"] --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: DaemonSet metadata: name: traefik-ingress-controller spec: selector: matchLabels: name: traefik-ingress-controller template: metadata: labels: name: traefik-ingress-controller spec: hostNetwork: true containers: - args: - --configfile=/config/traefik.toml image: traefik:1.7.12 imagePullPolicy: Always name: traefik-ingress ports: - containerPort: 80 hostPort: 80 name: http protocol: TCP - containerPort: 443 hostPort: 443 name: https protocol: TCP volumeMounts: - mountPath: /config name: config volumes: - configMap: defaultMode: 420 name: traefik-conf name: config
It can be deployed by running the command
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/apache/cloudstack-kubernetes-provider/main/traefik-ingress-controller.yml
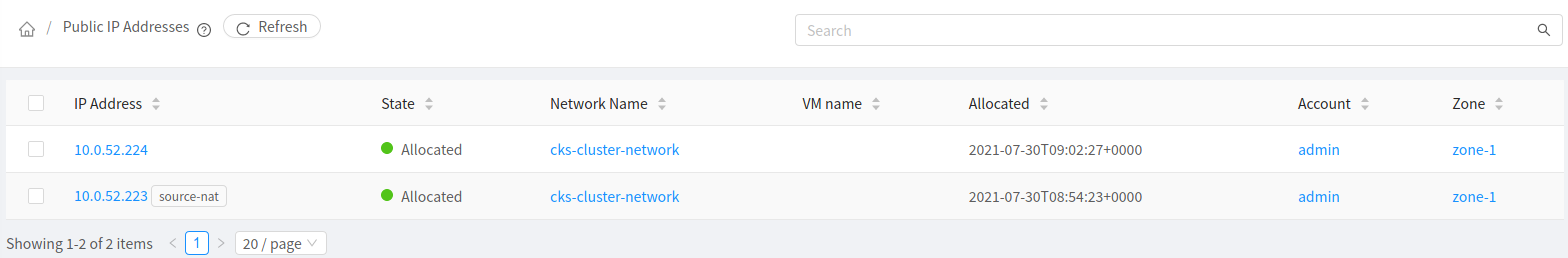
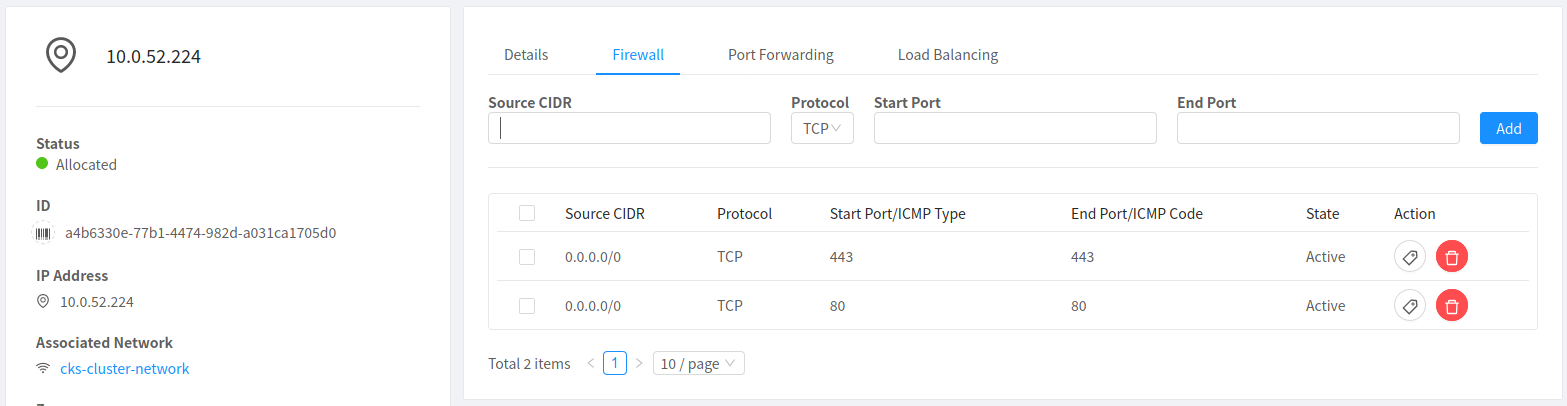
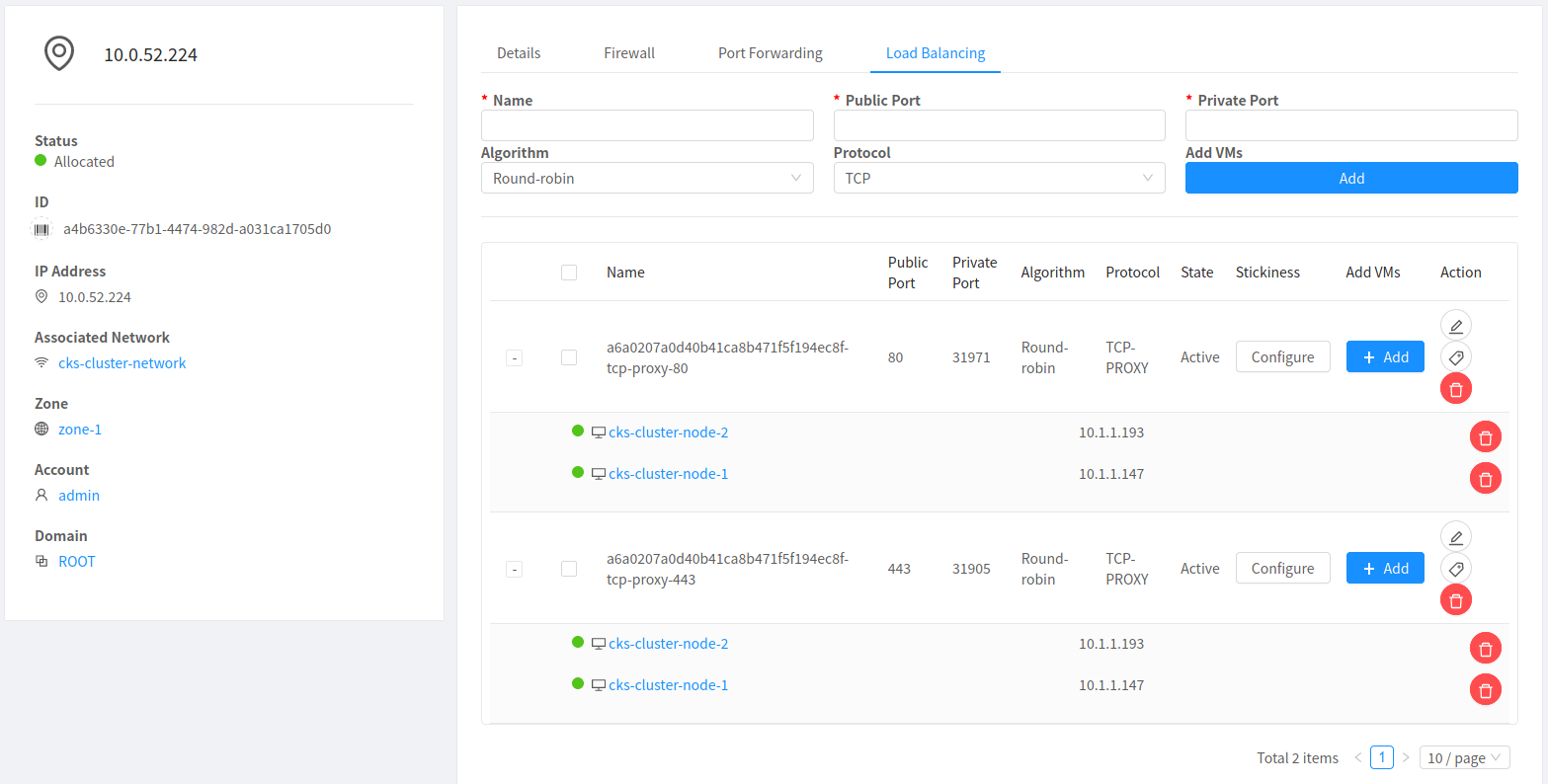
On successfully deploying the yaml file, a new Public IP Address in the same network as the cluster will be created. It will automatically have the firewall and port forwarding rules configured to distribute any traffic amongst the cluster worker nodes